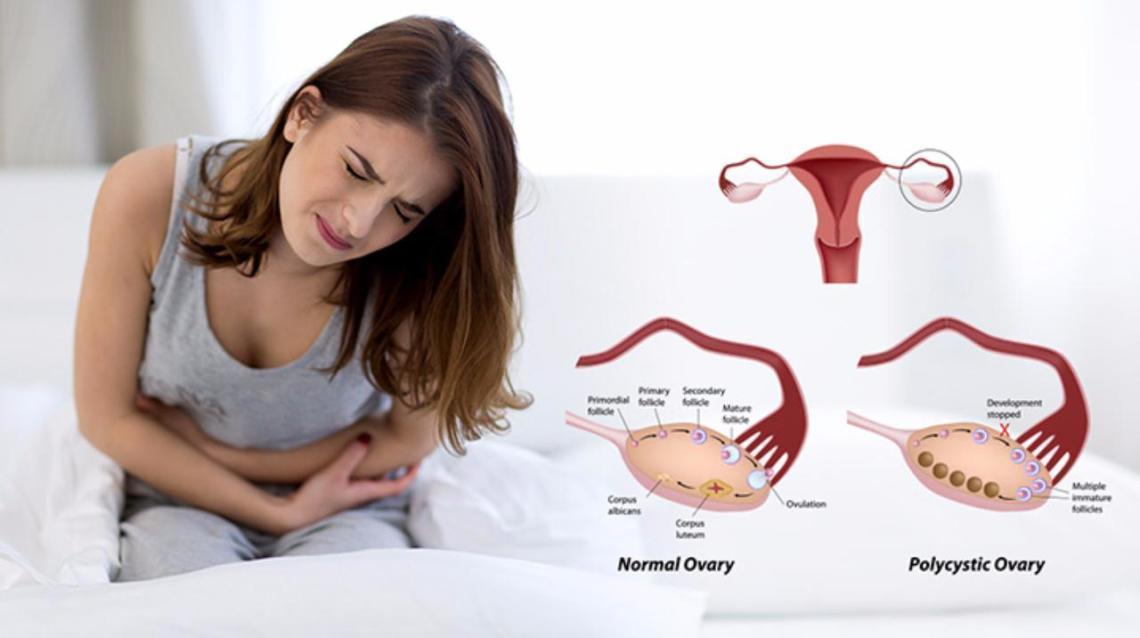
Women’s health encompasses the proactive measures, examination, identification, and management of conditions that specifically affect women. Among these conditions, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is highly common and likely to rank as the most frequently observed hormonal disorder in women of reproductive age.Most women who have PCOS experience anovulation, which leads to issues like infertility and abnormal menstrual bleeding.The PCOS Health Package offers patients the required diagnostic tests, consultations, and treatment regimens to correctly diagnose PCOS and manage its symptoms.In this blog, let’s delve into the PCOS package offered by Ankura Hospital.
What is PCOS?
PCOS, or Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome, affects various aspects of a woman’s well-being, characterizing it as a medical condition.This includes her menstrual cycle, fertility, hormonal balance, and physical appearance.PCOS can be categorized into four types: Insulin-resistant PCOS, Inflammatory PCOS, Hidden-cause PCOS, and Pill-induced PCOS.
Symptoms of PCOS
Missed or irregular menstrual cycles
Enlarged ovaries with numerous cysts
Excessive body hair growth on areas such as the chest, stomach, and back (hirsutism)
Weight gain, particularly around the abdomen
Acne or oily skin
Male-pattern baldness or hair thinning and
Difficulties with fertility
Causes of PCOS
PCOS has an unknown specific etiology. A few variables to consider are as follows:
Insulin resistance– The pancreas produces a hormone called insulin. Consequently, if you have an excessive insulin level, your body may produce too much androgen. This, in turn, can lead to difficulties with ovulation, which is the process of releasing eggs from the ovary.
Low-grade inflammation– In reaction to an infection or damage, white blood cells produce several substances. Low-grade inflammation is the term used to describe the response. PCOS patients experience a specific kind of chronic, low-grade inflammation that triggers androgen production in the polycystic ovaries.
Heredity– A family history of PCOS may contribute to the development of the disorder.
Excess androgen– In individuals with PCOS, the ovaries may produce high quantities of androgens, which hinder ovulation.
Diagnosis of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
An examination of the pelvis– This examination assesses the internal and exterior health of your reproductive organs.
Blood test– Blood tests can be used to measure hormone levels.
Abdominal ultrasound– An ultrasound can gauge the size of the ovaries and the endometrium, which lines the uterus.
If PCOS has been determined to be the root of your issue, your doctor could suggest more tests. These tests could be:
Routine examinations, such as assessments of blood count, hormonal and insulin levels, blood pressure, glucose tolerance, as well as measurements of cholesterol and triglyceride levels, are essential for comprehensive health monitoring.
Our PCOS package includes the following
HbA1C
Follicular Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Luteinising Hormone (LH)
Prolactin
Total Testosterone
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
Fasting Insulin
Gynecology consultation
The complete package can be availed at flat 30% discount.
Call now: 9053108108
HbA1C– A normal HbA1c score (5.4%) in PCOS individuals may be a sign of elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), which may lead to a cardio-vascular disease.
FSH and LH– This ratio typically ranges around 1:1, indicating that the blood levels of FSH and LH are comparable. However, in young, fertile women, FSH and LH frequently fall within the range of 4 to 8. Nevertheless, the LH to FSH ratio is frequently higher in women with polycystic ovaries, for instance, 2:1 or even 3:1. Consequently, patients with polycystic ovarian disease do not ovulate because of a high LH/FSH ratio.
Prolactin – Prolactin levels in women with PCOS are reportedly different from those in women without the condition. Furthermore, there are various ways that prolactin might result in infertility. To begin with, prolactin can prevent ovulation in females, causing their menstrual periods to stop.
Total Testosterone- Both the total and free testosterone levels are frequently higher in PCOS-afflicted women. Furthermore, a woman’s body’s naturally occurring menstruation and ovulation can be suppressed by even a slight increase in testosterone levels.
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone– TSH levels in women with PCOS are frequently normal (0.4–3.8 uIU/ml). However, doctors measure TSH levels to rule out other issues, such as an underactive or hyperactive thyroid, which often leads to irregular or absent periods and anovulation.
Fasting Insulin- To check for insulin resistance in women with PCOS, doctors should use a fasting blood glucose test. This is because elevated insulin levels may cause inflammation and other metabolic issues.
What is the primary method of treating PCOS?
To manage PCOS, many women require both medication and lifestyle adjustments. Additionally, your doctor will develop a treatment plan tailored to address your specific symptoms. Furthermore, for women who do not wish to become pregnant, the most popular PCOS therapy is birth control.
Feel free to reach out to our experienced gynecologists at Ankura Hospital for comprehensive guidance and support regarding PCOS. Our team is here to provide expert advice and personalized care to address your specific needs and concerns related to Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. We prioritize your well-being and are committed to assisting you on your journey towards better health.