What Are The Common Pediatric Dental Issues to Look Out For?
Cavities are known to be one of the most common chronic diseases in children across the world. Untreated cavities can cause pain and infections that may lead to problems with eating, speaking, playing and learning. Children who have poor oral health often miss more schools and receive lower grades than children who don’t. Therefore, it becomes necessary to consult a specialist in places like Ankura Hospitals for dealing with this problem effectively and effortlessly for the child.
- It has been found from a study that more than half children aged 6 to 8 have had a cavity in at least one of the baby teeth.
- More than half of adolescents aged 12 to 19 have had a cavity in at least one of their permanent teeth.
- Children aged 5 to 19 years from low-income families are twice as likely to have cavities from higher-income households.
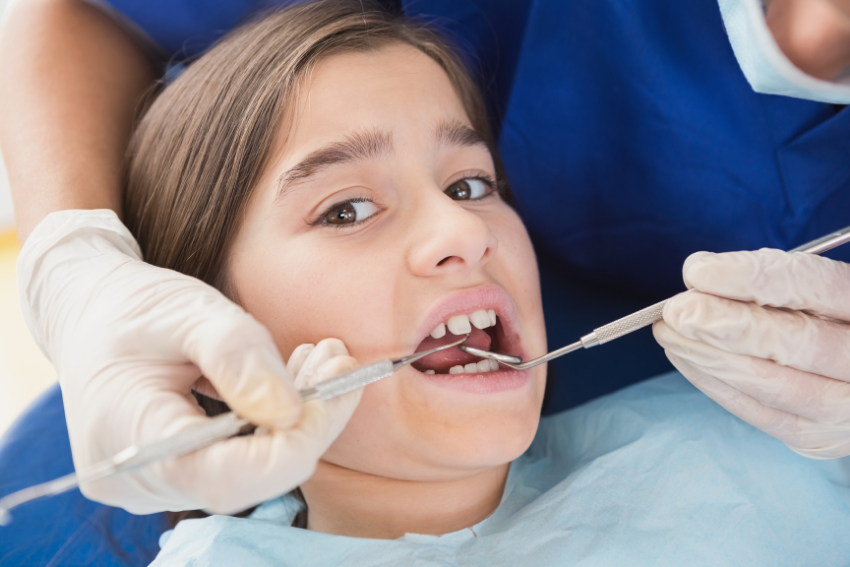
WHAT DENTAL PROBLEMS IS MY CHILD SUSCEPTIBLE TO?
Many of a kid’s dental problems are the same ones that affect adults, but your child’s teeth are still developing, and they’re softer and younger than their permanent successors. Untreated dental conditions can cause poor and misaligned teeth development, leading to more serious problems as a child grows up. Here are some of the problems they might face:
- Tooth Decay (Cavities)
Many young children aren’t proficient at brushing and flossing without supervision. Coupled with the fact that some kids might have a sugar-heavy diet, cavities can become a major issue. The acid in the plaque essentially eats away hard white enamel of the tooth, eventually wearing away the tooth.
- Tooth Sensitivity
Sensitive teeth are a dental problem that can be uncomfortable and distracting, often disrupting your child’s focus and routine. Some of the different things that can cause the child’s teeth to feel sensitive include:
- Areas of decay (cavities)
- Newly erupted permanent teeth
- Acid erosion and enamel wear
- Teeth grinding (bruxism)
- A cracked or missing filling
- Orthodontic treatment
In case of sensitive teeth, there’s a variety of treatments that can help reduce the pain and discomfort that the child is experiencing. If the sensitivity is caused by a dental-related problem, such as cavity, then it is recommended to visit the dentist right away to prevent the issue from becoming worse.
- Dental Emergencies
Kids playing sports, roughhousing with siblings, or falling while riding a bike are all scenarios in which a dental- related accident can arise. Some problems include- teeth chipping, breaking or cracking. In more severe circumstances, a permanent tooth may be knocked out completely. If the child’s permanent tooth falls out, immediately call the dentist for an emergency appointment and retrieve the tooth. Place the tooth in a glass of milk, saline solution, or clean water. The dentist may be able to place the permanent tooth back into the socket, allowing it to reattach with the help of a retainer.
- Pediatric Gingivitis and Gum Disease
Gum diseases not only affect adults, but are also common in children. Gingivitis and gum disease can occur in children and are actually quite common in pediatric dental patients. Gingivitis is the precursor to swollen gums, and slight bleeding when the child brushes or flosses. Gum disease is more aggressive in children with poor oral hygiene. It often involves pain in the mouth, gum recession, and areas of swelling. In most cases, gingivitis and gum disease could be avoided if more care is taken to brush and floss daily.
- Orthodontic Problems
Children rarely have perfectly straight teeth without any straight intervention. Luckily, there are many orthodontic treatments available to help the child or teen smile with confidence. Orthodontic problems are often a result of genetics, with the size and shape of the jaw playing a role in how the child’s teeth grow and come together. Some common misalignment issues seen in children include an overbite, underbite, open bite, and spacing problems.
- Excessive Thumb Sucking
Many infants, toddlers, and small children resort to thumb-sucking and pacifier use as a means to soothe anxiety. It doesn’t really become a dental problem until the child with ths habit as prolonged thumb sucking can cause issues with the way a child’s teeth develop because of this, parents should not allow the habit to continue past the toddler stage.
- Dental Anxiety and Phobias
The kids are often fearful when it comes to dentist appointments. Dental anxiety makes it more challenging to get the child in for the routine dental checkups and teeth cleanings. It can also stay with them into adulthood, affecting dental health in significant ways. The best way to combat dental anxiety in children is to make the experience relaxed, fun, and enjoyable.
- Grinding
This is an involuntary habit in most babies and toddlers. Children may clench or grind their teeth due to some discomfort in their jaws when their primary teeth start to emerge. However, children stop doing it after their teeth develop. But some children may continue grinding their teeth and risk the chances of eroding their tooth enamels. This can result in tooth decay or even or even sensitive teeth.
- Bad breath
It is also known as halitosis, and bad breath can affect anyone, regardless of their age. However, chronic bad breath in children could indicate a deeper root issue than eating stinky foods. It is ultimately caused by bacteria that live in the mouth. These bacterial colonies feed on leftover food, fluid and plaque – as they eat, they produce hydrogen sulfide, which leads to a bad smell in the mouth. As with adults, bad breath is most common in children in the morning, after they wake up.
- Baby teeth loss
For many children, this is a natural stage of development. The first lost tooth is usually one of the middle front teeth, and it typically loosens around the age of six. Generally, molars aren’t lost until a child is between 10 and 12, and most children have their full set of 28 permanent teeth by the time they’re 13 years old.
Understanding common pediatric dental problems and why they happen will help the parents and the child to know how to prevent them. Working on these as soon as they are detected can help the child and the parent to make it easy for both of them to grow out of them easily. Reach out to a reliable pediatric dental specialist for your Child’s problems.
